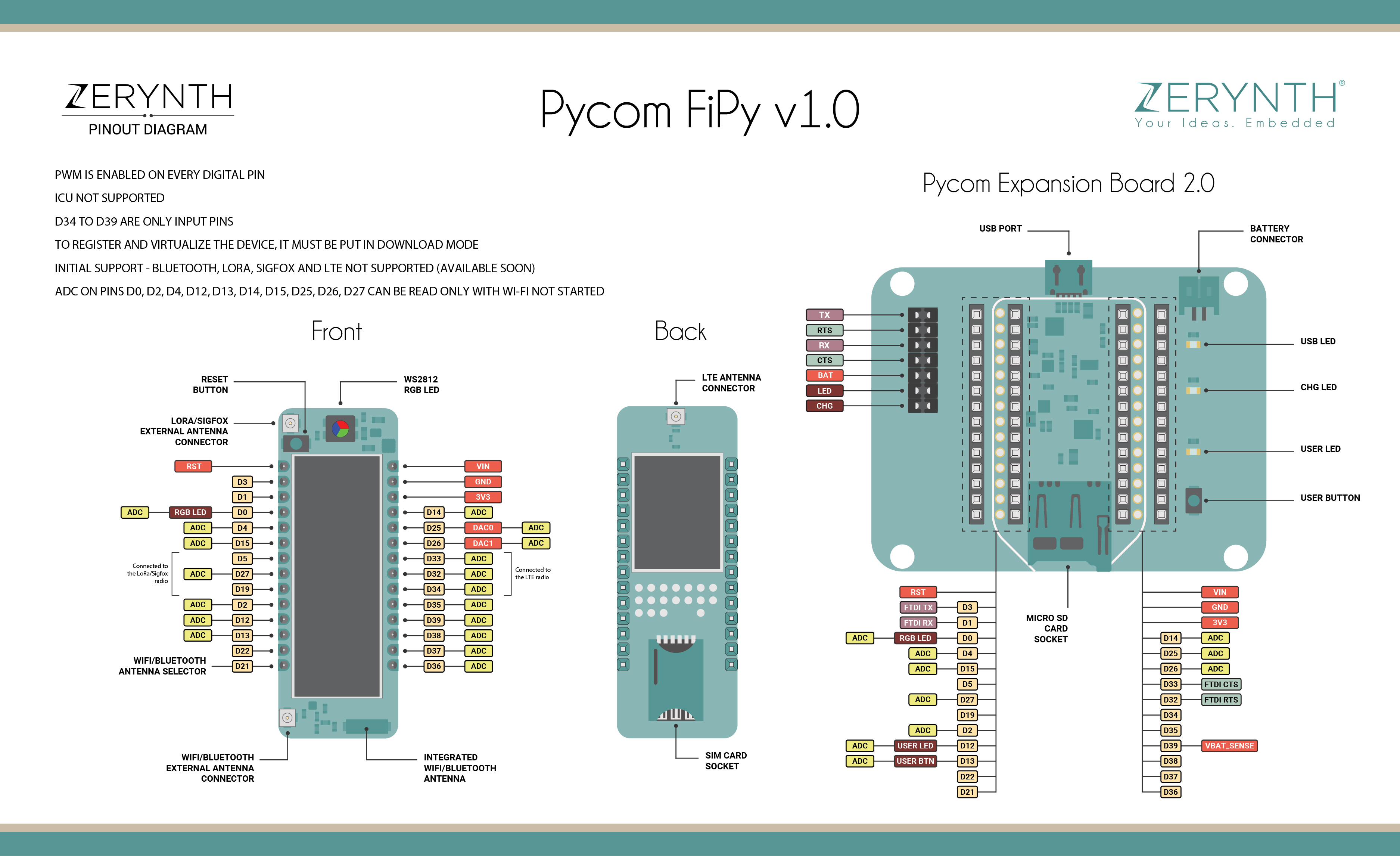
Pycom FiPy 1.0¶
FiPy 1.0 is a low-power consumption development hardware designed for Internet of Things (IoT) by Pycom. Pycom Fipy 1.0 integrates WiFi, Bluetooth, LoRa, Sigfox and dual LTE-M (CAT M1 and NBIoT) in one tiny board (same small foot-print as WiPy).
Pycom Fipy 1.0 features a Dual-Core ESP32 microcontroller, which supports Wi-Fi &Bluetooth dual-mode communication.
Warning
To be programmed, the Pycom Fipy 1.0 device needs the related expansion board or shields that expose its serial port (expansion board and shields available can be found here)
Flash Layout¶
The internal flash of the ESP32 module is organized in a single flash area with pages of 4096 bytes each. The flash starts at address 0x00000, but many areas are reserved for Esp32 IDF SDK and Zerynth VM. There exist two different layouts based on the presence of BLE support.
In particular, for non-BLE VMs:
| Start address | Size | Content |
|---|---|---|
| 0x00009000 | 16Kb | Esp32 NVS area |
| 0x0000D000 | 8Kb | Esp32 OTA data |
| 0x0000F000 | 4Kb | Esp32 PHY data |
| 0x00010000 | 1Mb | Zerynth VM |
| 0x00110000 | 1Mb | Zerynth VM (FOTA) |
| 0x00210000 | 512Kb | Zerynth Bytecode |
| 0x00290000 | 512Kb | Zerynth Bytecode (FOTA) |
| 0x00310000 | 512Kb | Free for user storage |
| 0x00390000 | 448Kb | Reserved |
| 0x00392000 | 4Mb | Free for user storage |
For BLE VMs:
| Start address | Size | Content |
|---|---|---|
| 0x00009000 | 16Kb | Esp32 NVS area |
| 0x0000D000 | 8Kb | Esp32 OTA data |
| 0x0000F000 | 4Kb | Esp32 PHY data |
| 0x00010000 | 1216Kb | Zerynth VM |
| 0x00140000 | 1216Kb | Zerynth VM (FOTA) |
| 0x00270000 | 320Kb | Zerynth Bytecode |
| 0x002C0000 | 320Kb | Zerynth Bytecode (FOTA) |
| 0x00310000 | 512Kb | Free for user storage |
| 0x00390000 | 448Kb | Reserved |
| 0x00392000 | 4Mb | Free for user storage |
Device Summary¶
Microcontroller: Tensilica 32-bit Single-/Dual-core CPU Xtensa LX6
Operating Voltage: 3.3V
Input Voltage: 5.5 to 3.3 V
Digital I/O Pins (DIO): 31
Analog Input Pins (ADC): 7
Analog Outputs Pins (DAC): 2
UARTs: 3
SPIs: 2
I2Cs: 3
Flash Memory: 8 MB
SRAM: 4MB
Clock Speed: 240 Mhz
Wi-Fi: IEEE 802.11 b/g/n/e/i:
- Integrated TR switch, balun, LNA, power amplifier and matching network
- WEP or WPA/WPA2 authentication, or open networks
Power¶
Power to the Pycom Fipy 1.0 is supplied directly via the “VIN” pin (5.5 V max voltage). Connecting it to one of available Pycom Expansion Board / Shields, it is possible to power up the device throught the USB Micro B connector or throught the battery connector (3.7/4.2 V Li-Po battery).
The power source is selected automatically and, if both power sources are provided, battery charge system will be enabled.
The device can operate on an external supply voltage of 3.3 to 5.5 volts. If using more than 5.5V, the voltage regulator may overheat and damage the device.
Connect, Register, Virtualize and Program¶
The Pycom Fipy 1.0 needs the related Pycom Expansion Board or Shields to be programmed.
The Pycom Expansion Board comes with the FT234XD Serial-to-usb chip on-board that allows opening the UART of the ESP32 chip. Drivers may be needed depending on your system (Mac or Windows) and can be download from here.
The Pycom Shields, instead, feature an USB to serial converter that should work out of the box for Windows 8/10/+, Mac and Linux platforms; for Windows 7 platform, drivers must be installed and can be found here.
Note
For Linux Platform: to allow the access to serial ports the user needs read/write access to the serial device file. Adding the user to the group, that owns this file, gives the required read/write access:
- Ubuntu distribution –> dialout group
- Arch Linux distribution –> uucp group
Once connected on a USB port, if drivers have been correctly installed, the Pycom Fipy 1.0 device is recognized by Zerynth Studio. The next steps are:
- Select the Pycom Fipy 1.0 on the Device Management Toolbar (disambiguate if necessary);
- Put the Pycom Fipy 1.0 in Download Mode (Boot mode):
- Open the Serial Monitor;
- Connect a jumper between GND and D0;
- Press Reset on-board button; ESP32 SDK messages must appear on the serial monitor, confirming that the device is in “Download mode”;
- Remove the jumper and Close the serial monitor;
- Register the device by clicking the “Z” button from the Zerynth Studio;
- Create a Virtual Machine for the device by clicking the “Z” button for the second time;
- Virtualize the device by clicking the “Z” button for the third time.
Note
During the Registration procedure, press the Reset on-board button when asked.
Important
To put the Pycom device in “Download Mode”, a jumper between GND and D0 pin must be connected. GND and D0 pins are available in 2 different ways according to the expansion board or shield used to program the Pycom device.
- Pycom Expansion Board –> GND and D0 pins are available on its parallel headers (see Pin Mapping section);
- PySense and PyTrack Shields –> GND and D0 are available on their External IO 2x5 Header (pin 1 and pin 5);
After virtualization, the Pycom Fipy 1.0 is ready to be programmed and the Zerynth scripts uploaded. Just Select the virtualized device from the “Device Management Toolbar” and click the dedicated “upload” button of Zerynth Studio and reset the device by pressing the Reset on-board button when asked.
Important
To exploit the Wi-Fi chip functionalities of the Pycom Fipy 1.0, the lib.espressif.esp32net library must be installed and imported on the Zerynth script.
Firmware Over the Air update (FOTA)¶
The Firmware Over the Air feature allows to update the device firmware at runtime. Zerynth FOTA in the Pycom Fipy 1.0 device is available for bytecode and VM.
Flash Layout is shown in table below:
| Start address | Size | Content |
|---|---|---|
| 0x00010000 | 1Mb | Zerynth VM (slot 0) |
| 0x00110000 | 1Mb | Zerynth VM (slot 1) |
| 0x00210000 | 512Kb | Zerynth Bytecode (slot 0) |
| 0x00290000 | 512Kb | Zerynth Bytecode (slot 1) |
For BLE VMs:
| Start address | Size | Content |
|---|---|---|
| 0x00010000 | 1216Kb | Zerynth VM (slot 0) |
| 0x00140000 | 1216Kb | Zerynth VM (slot 1) |
| 0x00270000 | 320Kb | Zerynth Bytecode (slot 0) |
| 0x002C0000 | 320Kb | Zerynth Bytecode (slot 1) |
For Esp32 based devices, the FOTA process is implemented mostly by using the provided system calls in the IDF framework. The selection of the next VM to be run is therefore a duty of the Espressif bootloader; the bootloader however, does not provide a failsafe mechanism to revert to the previous VM in case the currently selected one fails to start. At the moment this lack of a safety feature can not be circumvented, unless by changing the bootloader. As soon as Espressif relases a new IDF with such feature, we will release updated VMs.
Secure Firmware¶
Secure Firmware feature allows to detect and recover from malfunctions and, when supported, to protect the running firmware (e.g. disabling the external access to flash or assigning protected RAM memory to critical parts of the system).
This feature is strongly platform dependent; more information at Secure Firmware - ESP32 section.
zerynth secure socket¶
To be able to use zerynth secure socket on esp32 boards native_mbedtls: true must be used instead of zerynth_ssl: true in the project.yml file.
Missing features¶
Not all IDF features have been included in the Esp32 based VMs. In particular the following are missing but will be added in the near future:
- Touch detection support